Anthracite coal is widely recognized as one of the highest-quality solid fuels available today. With its high fixed carbon content, low volatile matter, and clean-burning characteristics, anthracite plays an important role in industrial energy supply, metallurgical processes, and environmental applications.

This article provides a comprehensive overview of anthracite coal and how briquetting technology enhances its industrial value. From material properties and industrial benefits to cold briquetting processes and performance factors, this article aims to help industrial users better understand how to maximize the value of anthracite coal.
What Is Anthracite Coal?
Anthracite is the highest rank of coal, formed over millions of years under extreme metamorphism.

Its superiority over bituminous coal or lignite is defined by three core pillars:
High Energy Density and Stable Combustion Performance
Anthracite offers the highest energy density among coal types, allowing more heat to be generated per unit mass. Its stable combustion behavior makes it suitable for industrial furnaces, boilers, and kilns that require consistent thermal output.
Low Volatile Matter and Clean-Burning Characteristics
With minimal volatile content, anthracite burns with little smoke, soot, or odor. This helps improve workplace conditions and reduces environmental impact.
Low Ash and Sulfur Content for Equipment Protection
Low ash and sulfur levels reduce slag formation, corrosion, and fouling, extending the service life of combustion equipment and lowering maintenance costs.
What is Anthracite Coal Used for
From heavy industry to environmental protection, anthracite’s versatility is unmatched:
Metallurgy & Steelmaking: Acts as a premium reducing agent and carbon source in blast furnaces and Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF). It is an excellent, cost-effective partial substitute for coke.

Water Filtration: Due to its high density and porosity, crushed anthracite is a standard medium for drinking water and wastewater treatment.
High-Efficiency Heating: Ideal for industrial boilers and district heating systems requiring consistent thermal performance.
What Is Anthracite Coal Briquettes and Why It Matters
Anthracite coal briquettes are engineered fuel units created by compressing anthracite fines or powder into dense, uniform shapes using briquetting technology.
In the coal supply chain, up to 30% of anthracite is often lost as “fines” (dust and small particles) during mining and transport. These fines are difficult to burn directly due to poor airflow and high material loss. Briquetting is the essential link that restores the industrial utility of this material.

Why it matters:
Optimized Combustion Efficiency: Unlike loose powder, uniform briquettes create consistent interstitial spaces in a furnace, allowing for superior airflow and more complete, stable combustion.
Minimized Material Loss: High-strength briquettes eliminate dust clouds and fine leakage, significantly reducing waste during handling, storage, and long-distance transport.
Strategic Cost Savings: By converting low-value coal byproducts into a high-performance, easy-to-handle fuel, plants can maximize their return on every ton of coal purchased.
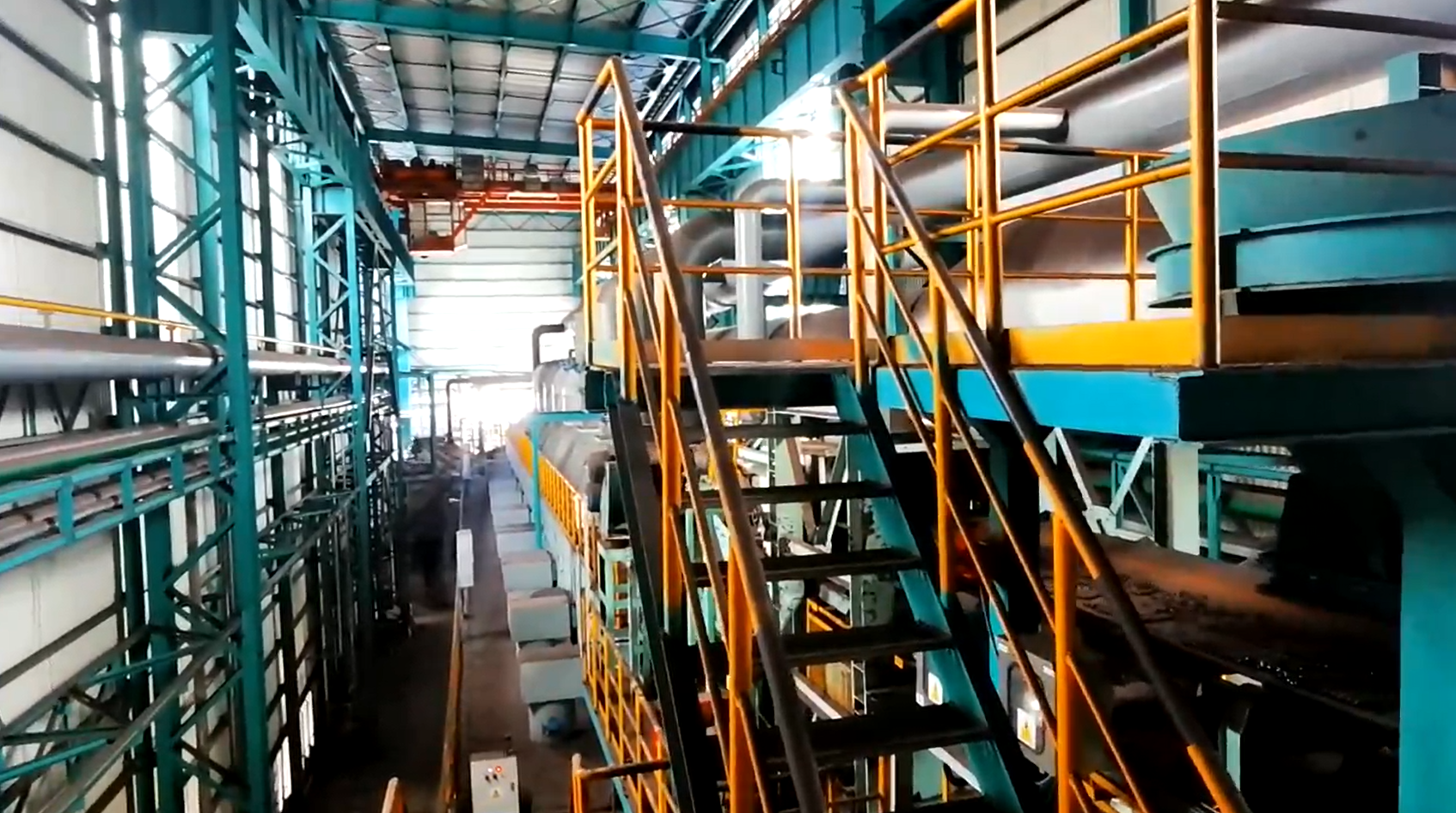
How to Make Anthracite Coal Briquettes: Briquetting Process
The production of anthracite coal briquettes typically follows a cold briquetting process consisting of several key steps.
Raw Material Preparation and Particle Size Control
Anthracite coal is crushed and ground to an appropriate particle size to ensure uniform mixing and effective compaction during pressing.
Binder Selection for Anthracite Coal Briquettes
Mix the coal particles with a binder (such as starch, molasses, or lignosulfonate) to enable cohesion.
Briquetting Machine and High-Pressure Forming
The mixed material is compressed using briquetting machines, such as hydraulic or roller presses, to form briquettes with uniform shape and density.
Drying and Curing of Anthracite Briquettes
After forming, briquettes are dried and cured, often using mesh belt dryers, to remove residual moisture and stabilize their structure.
Applications of Anthracite Coal Briquettes in Industry
Anthracite briquettes are widely used in applications that require efficient fuel utilization and controlled combustion.

Industrial Furnaces, Boilers, and Kilns
Uniform briquette size and density enable consistent feeding and combustion in industrial thermal systems.
Metallurgical Reduction and Deoxidation Processes
Anthracite briquettes can be used as reducing agents in electric arc furnaces (EAF) and non-ferrous metal smelting, such as tin production based on SnO₂. In steelmaking, briquettes also act as effective deoxidizers.
Water Treatment and Filtration Media
Due to their structural stability and porosity, anthracite briquettes and granules are also applied in water purification systems.
Key Factors Affecting Anthracite Briquette Performance
Although anthracite coal has excellent inherent properties, briquette performance depends on several controllable factors.
Moisture Content and Drying Control
Excess moisture reduces briquette strength and combustion efficiency. Proper drying is essential to ensure stable performance.
Binder Type, Dosage, and Briquette Strength
Binder quality directly affects the qualification rate and mechanical strength of briquettes.
Storage and Handling Conditions
Anthracite briquettes should be stored in dry, well-ventilated environments to prevent moisture absorption and performance degradation.
Jianjie Integrated Solution for Anthracite Briquetting
In industrial anthracite briquetting, binder selection plays a critical role in determining briquette strength, forming stability, and overall qualification rate.
The performance of a dedicated binder for anthracite briquetting is closely linked to material characteristics and process conditions, and optimized combinations can lead to significantly higher production stability and success rates.

Jianjie High-Performance Binders for Anthracite Briquetting offer:
- Low Dosage, High Strength
Typically achieved with only 1–4% addition, maintaining the coal’s original purity.
- Reliable Thermal and Structural Stability
With optimized binder dosage, briquettes produced at a ratio of approximately 35–50 tons per ton of binder maintain stable structure during high-temperature smelting operations.
- High Briquette Qualification and Mechanical Strength
Under optimized conditions, briquette forming rates can reach around 98%. Wet briquettes remain intact after multiple 1.5-meter drop tests, while dried briquettes typically achieve compressive strength above 80 kg, meeting the requirements for handling, transport, and industrial use.
Integrated Technical Support: In addition to supplying binders, Jianjie provides one-stop technical services covering material testing, binder formulation adjustment, and on-site briquetting machine optimization.
This integrated approach helps ensure stable operation and improved efficiency across the entire briquettes production line.
Conclusion: Maximizing the Value of Anthracite Coal Through Briquetting
Anthracite briquetting is a strategic move for industries seeking to optimize costs and meet environmental goals. By combining premium coal properties with advanced briquetting technology, you transform anthracite fines into a high-performance energy asset.
Ready to stabilize your production and reduce costs? Contact Jianjie’s Technical Team for a tailored consultation and material testing.
FAQs About Anthracite Coal Briquettes
Q: How is Anthracite Coal Formed?
A: Anthracite coal is formed through long-term coalification under high temperature and pressure. As moisture and volatile matter are removed, the material becomes dense and rich in fixed carbon, resulting in clean-burning behavior and high energy value.
Q: What is the Difference between Anthracite and Bituminous Coal?
A: The main difference between anthracite and bituminous coal is their carbon content and combustion behavior.
Anthracite contains much higher fixed carbon and lower volatile matter, which allows it to burn more cleanly with less smoke and more stable heat output.
Bituminous coal ignites more easily but produces higher emissions and ash, making it more suitable for applications where lower cost and easier ignition are prioritized.
Q: What are the typical applications of anthracite briquettes?
A: Anthracite briquettes are commonly used in industrial furnaces and boilers, metallurgical reduction and deoxidation processes, and water filtration and environmental applications.
Q: Can anthracite briquettes fully replace coke in smelting?
A: While specific processes vary, anthracite briquettes are highly effective as a partial coke substitute, significantly reducing raw material costs while maintaining high reduction efficiency.







Tinggalkan Balasan