As the world moves towards smarter and more sustainable resource utilization, coal briquetting has emerged as a cost-effective, eco-friendly solution to reduce waste, improve fuel efficiency, and streamline coal handling. In this article, we will explore what coal briquettes are, how they’re made through cold briquetting technology, the different types of coal used, the challenges involved, and how tailored binders for coal briquettes from Jianjie can help overcome them.
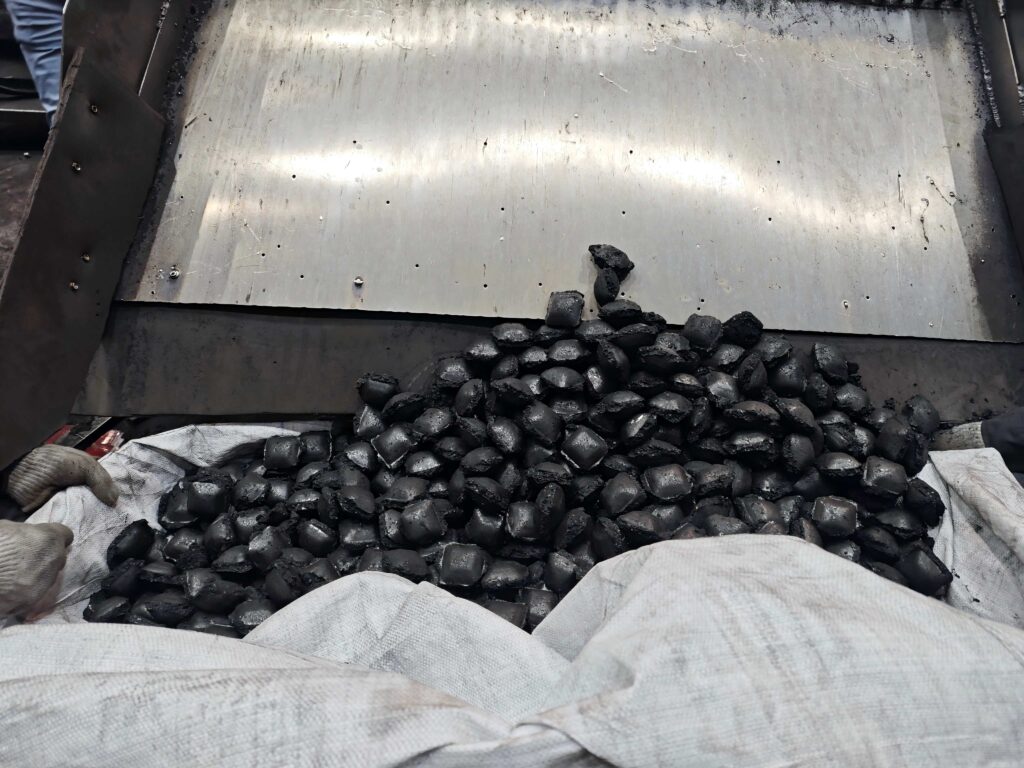

Coal Briquettes
What Are Coal Briquettes?
Coal briquettes are compacted blocks or rounded balls made from coal dust, fine particles using coals in different grades. They are mixed with binders and pressed into uniform shapes—such as cylinders, ovals, pillows, or beehive hexagons, typically under ambient temperature in a process called cold briquetting. Coal briquetting technology transform loose, dusty coal into a clean-burning, transportable, and user-friendly fuel source.
Coal briquettes are used as an alternative to raw coal in various industrial and residential applications, including steelmaking, cement production, power generation, and household heating.
The production of coal briquettes typically follows a structured steps of briquetting to ensure uniform quality and performance:
- Raw material preparation: Pulverized coal is screened to remove oversized particles and impurities.
- Binder mixing: A binder is added to improve adhesion and briquette strength.
- Cold briquetting: The coal-binder mix is pressed into desired shapes using a briquette press.
- Curing or drying: Tthe briquettes are dried to enhance durability and shelf life. Unable to fully drying briquettes may casue breakage and crumble.
Cold briquetting is especially popular due to its low energy consumption (conducted at room temperature, no heating required) and the ability to handle a wide range of coal grades and particle sizes.
The primary benefits of briquetting coal include:
- Reduce dust for safer and more convenient handling and transport
- Stable combustion with more predictable heat profiles
- Easier storage and bulk handling via uniform shapes
Briquetting can improve efficiency and safety in the use of coals, especially when dealing with coal fines or low-rank grades.
What are the Types of Coal
The coals are categorized by their clean grade through the carbon content in the products. There are mainly four types of coals in the market: Anthracite, bituminous coal, lignite coal, peat (content grade and volatile matter from high to low).

cleaniness of coals
Different types of coals:
Anthracite coal: Anthracite is the highest rank of coal, with a carbon content ranging from 86% to 92%. It is hard, clean-burning, and has very low moisture content. Due to its high density and purity, anthracite can produce strong, high-quality briquettes.
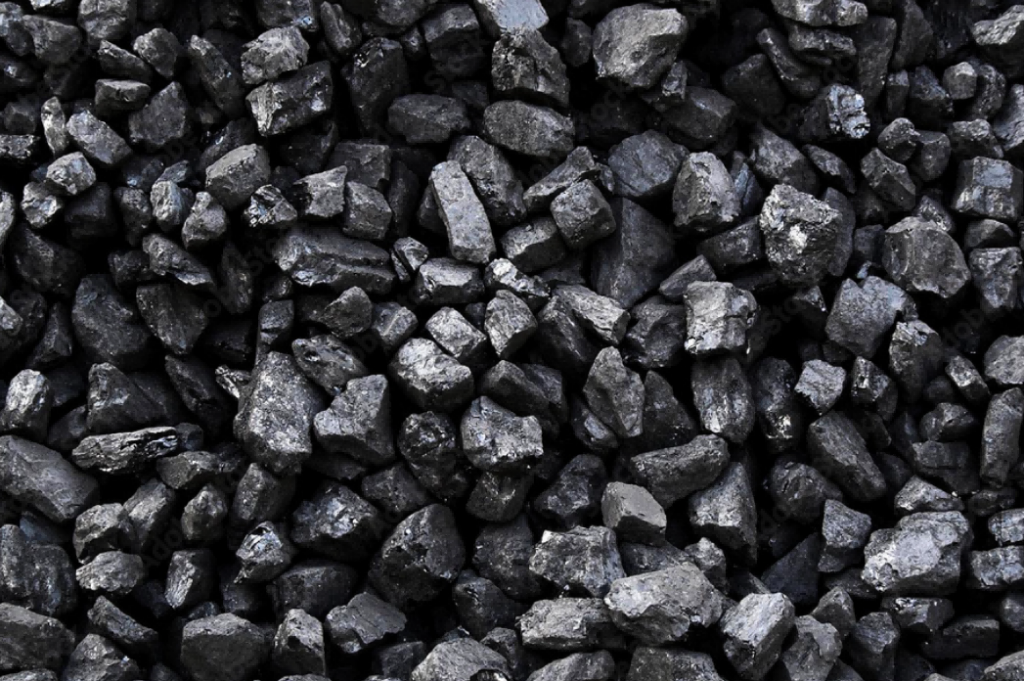

Anthracite coal
Bituminous coal: Bituminous coal is the second-highest rank of coal, with a carbon content ranging from 76% to 86%. It is widely used due to its abundance, moderate moisture content, and excellent compatibility with most briquetting binders. There are two main subtypes: thermal coal (also known as steam coal) and metallurgical coal. Thermal coal typically has a higher carbon content than metallurgical coal. Metallurgical coal is primarily used for coke production and is therefore also called coking coal.
Lignite coal (brown coal): Lignite contains approximately 65–70% carbon on a dry basis and has a moisture content of 35–55%. It is mainly used for power generation, often requiring pre-drying and the addition of binders for briquetting applications.
Peat: Peat represents the earliest stage of coal formation, with the highest moisture content and the lowest carbon content—less than 60%. While it is less energy-dense than other types of coal, peat is still used in some regions for domestic heating purposes.
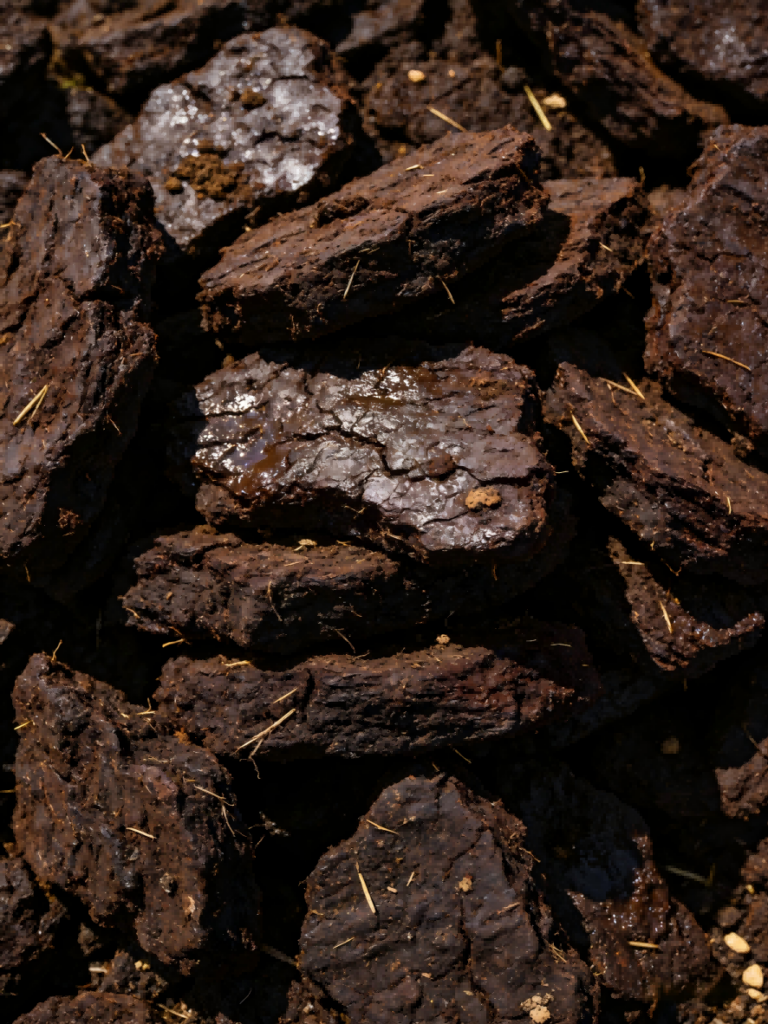

Peat
Choosing the right coal type will influence overall briquette performance.
Applications of Coal Briquettes
The use of coal briquettes spans a wide range of industrial and domestic sectors thanks to their convenience, energy density, and environmental advantages.
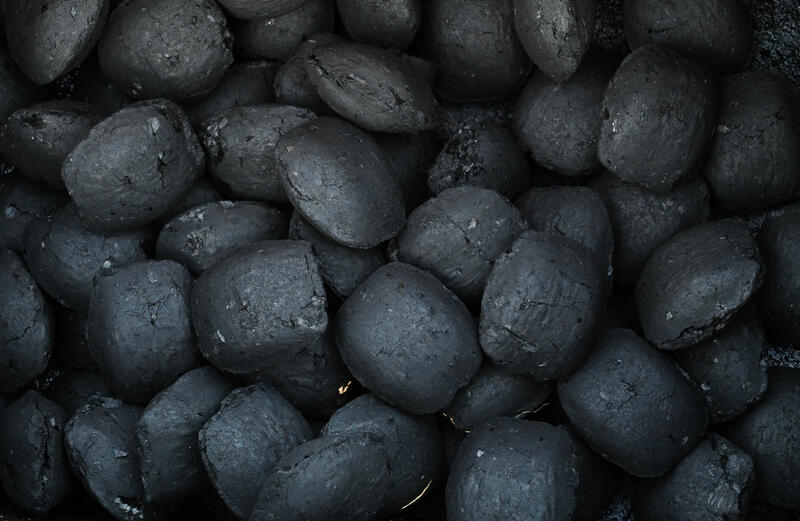

Coal briquettes
Industrial Use:
- Metallurgy: Coal briquettes are a clean and efficient fuel source for iron and steel production, particularly in blast furnaces and sintering operations.
- Cement and lime kilns: Uniformly sized briquettes provide consistent combustion and even heat distribution, improving kiln efficiency.
- Thermal power plants: Briquettes offer a practical alternative to loose coal, especially in facilities focused on recovering coal fines.
- Coal Gasification: High-quality briquettes serve as ideal feedstock for producing synthetic natural gas (SNG) through gasification processes.
Domestic Use:
- Heating and Cooking: In some regions, coal briquettes are still used for residential space heating and cooking, thanks to their easy handling, storage, and longer burn time compared to loose coal.
By converting coal fines and low-grade coal into briquettes, industries can reduce waste, lower dust emissions, and simplify logistics.
Challenges in Briquetting Coal

Though the cold briquetting process is efficient, coal’s natural variability presents several challenges:
High moisture content: Particularly in lignite and peat which contain high moisture before drying. They need to undergo appropriate drying before briquetting. High moisture content will make the briquettes prone to breakage.
Low reactivity or high density: Like in anthracite coal, requiring more pressure and stronger binders.
High Volatile Matter: Coal with high volatile matter will produce smoke and pollute the air and environment.
Ash and sulfur content: Can affect combustion performance and environmental compliance.
Fine particle segregation: Leads to inconsistent bonding and weak briquettes.
Storage stability: Some briquettes absorb moisture or degrade over time without proper curing or additives.
Effective binder formulation, moisture management, and pressure optimization are key to overcoming these issues.
Factors That Affect the Quality of Coal Briquettes
Even with proper raw material and equipment, many briquettes suffer from poor durability. As explained in our technical article Why Are Your Briquettes Fragile? Key Factors That Affect Briquette Quality, several critical factors influence final product strength:
- Binder type and ratio
- Mixing uniformity
- Moisture content
- Compression pressure
- Curing or drying conditions
Understanding and adjusting these variables can significantly reduce cracking, crumbling, and dusting—leading to stronger, transportable briquettes.
Choosing the Right Binder for Coal Briquettes
Binders are the backbone of cold briquetting—they help a briquette holds together. A good binder for coal briquettes should:
- Provide high binding strength with minimal dosage
- Be compatible with various coal grades
- Withstand thermal shock and water exposure
- Be safe and environmentally compliant
- Enable smooth processing at scale
Common binder types include organic compounds (like starch, molasses, polymer-based), inorganic materials (such as cement or clay), or composite solutions.
The right binder for coal briquettes depends on your coal type, briquetting process, application scenario, and cost-performance goals.
For coal briquettes, there are requirements toward heat resistance and impurities grade. Therefore, composte binder can be a great option for coal briquettes as it increases the high temperature resistance compared to organic binder and reduces the impurities compared to inorganic binders.
Summary
Cold briquetting is a powerful solution for coal utilization, but success depends on mastering the right materials, technology, and binder chemistry. Whether you’re struggling with moisture, strength, or coal variation—Jianjie Group delivers tested, high-performance binders for every challenge.
At Jianjie Group, we offer a complete range of tailored binder solutions designed specifically for coal briquetting. Our products are:
Technically optimized – For specific coal types like bituminous, lignite, or anthracite
Eco-friendly – Non-toxic, low-emission, and worker-safe
Field-proven – Tested in various industrial scenarios for strength and weather resistance
Cost-effective – Minimal usage needed for maximum performance
Nee help with coal briquettes? Contact us now for technical solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Coal Briquettes and Binders
1. What are coal briquettes used for?
Coal briquettes are widely used in metallurgy (e.g. steelmaking), cement kilns, power plants, and domestic heating. They provide a cleaner, more efficient way to use coal fines or low-grade coal.
2.What type of coal is best for making briquettes?
Bituminous coal is commonly used due to its high energy content and moderate moisture. However, lignite, anthracite, and even peat can be used with the right binder for coal briquettes and optimized pressing conditions.
3. Why do my coal briquettes break or crumble easily?
Poor briquette strength can result from:
- Low binder dosage
- Improper mixing
- Incorrect moisture content
- Inadequate pressure or curing
Read our full guide: Why Are Your Briquettes Fragile?




-scaled.jpg)